Network tokens are unique identifiers used in place of card details during transactions. They enhance security by keeping sensitive information hidden. This article from VGS explains how network tokens work, their benefits, and their importance in payments.
- Network tokens enhance payment security by replacing sensitive card information with unique digital identifiers, significantly reducing the risk of fraud.
- The dynamic nature of network tokens allows automatic updates, ensuring seamless transactions even when card details change, which is especially beneficial for recurring payments.
- Adopting network tokenization improves authorization rates and customer experience while reducing compliance burdens and operating costs for businesses.

Understanding Network Tokens
Network tokens are unique digital identifiers that replace primary account numbers (PANs) during transactions. These tokens are designed to act as payment credentials linking a card to a specific merchant, ensuring that sensitive PAN information is never transmitted. This innovative approach drastically reduces the risk of fraud, as the actual card details are never exposed during the transaction process. Importantly, if a card number changes, due to expiration or reissuance, the associated token is automatically updated, ensuring seamless continuity for merchants and consumers.
Substituting PANs with network tokens significantly enhances the security of the payment process. Each transaction utilizes a different token, making it nearly impossible for cybercriminals to steal and misuse card information. This method not only enhances security but also builds trust between merchants and consumers, knowing that their payment information is well-protected.

How Network Tokenization Works
Network tokenization is a sophisticated process managed by card networks that generate tokens in real-time for secure transactions. The process involves:
- When a transaction is initiated, the payment service provider requests a network token from the card scheme.
- The card scheme replaces the sensitive credit or debit card data with a unique identifier (token).
- This token is accompanied by a unique cryptogram, adding an additional layer of security during the transaction.
- If a card number changes, due to expiration, loss, or reissuance, the associated token is automatically updated by the network, ensuring uninterrupted payments without requiring the consumer to re-enter their card details.
The card issuer plays a crucial role in this process by verifying the card details before the transaction is authorized. This ensures that all qualifying transactions, including card-not-present transactions and card payments, are legitimate and secure, whether they are conducted online or as recurring payments.
The dynamic nature of network tokens, which can be updated automatically, ensures that transactions remain seamless even if the underlying card details change.

Difference Between Network Tokenization and PCI Tokenization
While both network tokenization and PCI tokenization aim to secure payment data, they operate differently within the payment ecosystem. Let's break it down.

Network tokens are a set of randomized code that act as a substitute for a credit card's primary account number (PAN). Network tokens allow merchants to securely process payments without storing sensitive card details, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches while increasing token interoperability among PSPs. These tokens are issued and managed by the major card networks themselves, such as Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover.
In contrast, PCI-compliant tokens are surrogate values that replace sensitive cardholder data, such as the Primary Account Number (PAN), to help businesses reduce their PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance scope. These tokens are generated by a tokenization system. Typically, these tokenization systems are provided by a secure payment processor or token vault, like VGS, and are used to safely store or transmit payment information without exposing the actual card data.
Key Benefits of Network Tokenization
The benefits of network tokenization extend far beyond just enhancing security. By substituting primary account numbers with tokens, businesses can protect sensitive data, improve customer experience, and boost authorization rates. Network tokenization also helps businesses comply with PCI standards by minimizing the exposure of sensitive payment information.
Furthermore, businesses are increasingly adopting network tokenization to maximize conversion rates. Network tokens automatically update card data across networks, increasing authorization rates and successful transactions. This allows businesses to provide a more secure and seamless payment experience for customers. The following subsections will delve deeper into the specific benefits of network tokenization.

-
Enhanced Payment Security
Network tokens significantly enhance payment security by replacing sensitive information, such as card details, with unique identifiers, which protect account information from potential breaches. This process converts sensitive payment details into tokens, mitigating the risk of fraud and ensuring that merchants processing payments do not have access to sensitive credit card information.
Implementing network tokenization can potentially decrease merchants' PCI compliance burdens by limiting the exchange of sensitive data and adhering to PCI DSS requirements. Additionally, card networks update network tokens automatically, ensuring they remain valid even if the card details change, thus maintaining a secure and seamless transaction process.
-
Reduced Fraud Rates
Network tokens play a crucial role in securing payment data across all transaction stages, significantly lowering the risk of fraud. Each token generated for online purchases is unique to the retailer, limiting the impact of potential security breaches. Network token transactions enhance this security further, forming an essential part of the payments stack.
Companies like Visa have reported substantial savings in fraud losses due to their tokenization solutions, highlighting the effectiveness of this technology to reduce fraud and fraudulent activity.
-
Higher Authorization Rates
One of the most compelling benefits of network tokenization is its positive impact on payment authorization rates. On average, businesses experience a 3% increase in authorization rates when adopting network tokenization. This improvement is largely due to dynamically updated tokens that remain valid even if the primary account number changes, eliminating declines associated with expired account details.
Both Visa and Mastercard facilitate higher authorization rates through their tokenization services, potentially increasing merchant revenue by ensuring more successful transactions. Merchants adopting network tokenization can thus expect higher approval rates and increased revenue.
-
Cost Savings
Utilizing network tokens can lead to significant cost savings for businesses. By reducing transaction fees and interchange costs, network tokenization directly benefits the bottom line. Lower costs for processing tokens compared to traditional PANs result in reduced transaction costs, making it an economically viable option for merchants.
Additionally, merchants can mitigate rate increases related to non-token transactions by adopting network tokens, further contributing to overall cost savings. For example, when someone uses a PAN rather than a token, it can often carry higher fees or interchange rates. With NTs, networks typically reward this with lower processing fees that apply to non-tokenized payments.
This reduction in operating costs, combined with enhanced security and higher authorization rates, makes network tokenization a smart financial choice for businesses.
-
Improved Customer Experience
Network tokens enhance customer experience by ensuring that outdated PANs can still process payments, reducing transaction declines. This creates a smoother payment process and minimizes the need for customers to update their card information frequently.
Network tokenization provides a frictionless payment experience, reducing payment failures and enhancing security. This leads to higher customer satisfaction. Merchants using network tokens also benefit from reduced customer service issues related to transaction failures on old cards, further improving the overall customer experience.
Network Tokens in Recurring Payments
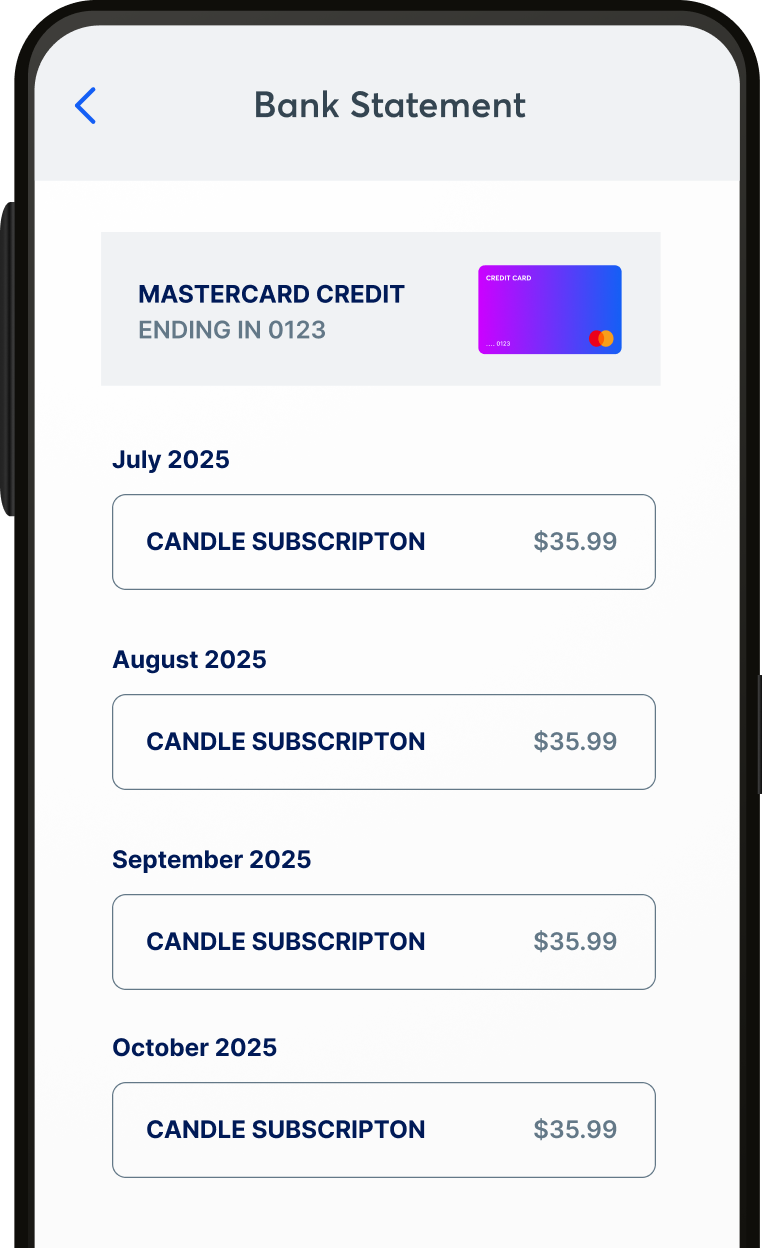
Network tokens are particularly beneficial for recurring payments. They help maintain updated payment credentials, reducing declines due to outdated card information. This automatic update feature ensures that subscription services remain uninterrupted, providing a seamless experience for customers.
Minimizing friction during the checkout process and reducing involuntary churn, network tokens contribute to a more efficient and customer-friendly payment system. This ensures that businesses can maintain consistent revenue streams without the disruptions caused by outdated payment information.

Adopting Network Tokenization
Adopting network tokenization allows businesses to automatically update card details when cards reach their expiry date or are replaced, ensuring a seamless transaction experience. This not only reduces the burden of PCI compliance but also helps in minimizing fraud and operating costs.
Integrating network tokenization allows merchants to improve authorization rates and offer a more secure and seamless purchasing experience for their customers. Reducing declined transactions due to outdated card information further enhances the overall efficiency of the payment process.


Role of Major Card Networks
Major card networks play a pivotal role in the creation and implementation of network tokens. Networks not only create the tokens, but they also make sure they are up-to-date via their connections to issuers. These networks responsible include:
Visa, for instance, has provisioned around 10 billion network tokens since the service's launch, showcasing its commitment to enhancing payment security.
Mastercard's Digital Enablement Service (MDES) supports the secure implementation of network tokens across various platforms, demonstrating the collaborative efforts of card networks to improve transaction security. These partnerships with payment networks are crucial for replacing sensitive card data with unique tokens, thereby enhancing overall security.
Real-World Applications of Network Tokens
Real-world applications of network tokenization are evident in popular payment systems like Apple Pay and Google Pay. Apple Pay uses tokenization to replace credit card details with tokens during transactions, significantly enhancing security. Similarly, Google Pay creates a pay token to represent a user's card number, minimizing the risk of account hacking.
These applications highlight the importance of network tokens in modern payment systems, where they play a crucial role in protecting sensitive card information and reducing fraud risk. The use of network tokens in these platforms exemplifies the practical benefits and enhanced security that tokenization offers.


Future of Network Tokenization
The future of network tokenization looks promising, with global transactions utilizing network tokens expected to double by 2029 for future use. Major card networks like Visa and Mastercard are aiming for almost complete token adoption by 2030, focusing on enhancing payment security and efficiency.
As businesses continue to adopt network tokenization, they can expect higher authorization rates, reduced fraud, and improved customer experience. The ongoing advancements in this field ensure that network tokenization will remain a cornerstone of secure and efficient payment processing in the years to come.
Summary
In summary, network tokenization offers a robust solution for enhancing payment security, reducing fraud, and improving customer experience. By replacing sensitive PANs with unique tokens, businesses can ensure that their payment processes are secure and efficient. The involvement of major card networks and the adoption of network tokenization by popular payment platforms like Apple Pay and Google Pay further underscore its significance.
As we look to the future, the continued adoption and innovation in network tokenization promise a safer and more efficient payment ecosystem. Embracing this technology is not just a smart choice but a necessary step towards securing the future of digital transactions.
Learn MoreFrequently Asked Questions
What is network tokenization?
Network tokenization enhances transaction security by replacing primary account numbers (PANs) with unique digital identifiers, known as network tokens. This thereby significantly reduces the risk of fraud, increases authorization rates, and enhances customer experience.
How does network tokenization improve payment security?
Network tokenization enhances payment security by transforming sensitive payment information into unique identifiers, which safeguards account details and minimizes the risk of data breaches.
What is the difference between network tokenization and PCI tokenization?
There are many differences is that network tokenization and PCI tokenization.
- Network Tokens are a set of randomized code that act as a substitute for a credit card's primary account number (PAN) and allow merchants to securely process payments without storing sensitive card details, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches while increasing token interoperability among PSPs. These tokens are issued and managed by the major card networks themselves. These networks include Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover.
- PCI-tokens are surrogate values that replace sensitive cardholder data, such as the Primary Account Number (PAN), to help businesses reduce their PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance scope. These tokens are generated by a tokenization system and third-party providers. Typically, these tokenization systems are provided by a secure payment processor or token vault, like VGS, and are used to safely store or transmit payment information without exposing the actual card data.
Many times, businesses use both network tokens and PCI-compliant tokens.
How do network tokens benefit recurring payments?
Network tokens enhance recurring payments by keeping payment credentials updated, minimizing declines from outdated card information, and ensuring seamless transaction authorization.
What role do major card networks play in network tokenization?
Major card networks play a crucial role in network tokenization by developing and enforcing standards for network tokens. Networks also create, manage, and provision them, even for updates. These standards significantly enhance payment security across multiple platforms, ensuring safer transactions for consumers and merchants alike.
Why would a business need network tokens?
A business would need network tokens to enhance security by reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud, and improving transaction approval rates. Tokens are updated automatically when card details change (such as after expiration or reissuance).
Additionally, network tokens support smoother customer experiences by ensuring stored payment methods remain valid, minimizing declined transactions and checkout friction.
Why would a business use a token service provider (TSP)?
A Token Service Provider (TSP) is a secure technology company responsible for generating, issuing, and managing payment tokens. A TSP manages the creation, provisioning, and lifecycle of payment tokens, which replace sensitive card data with secure, non-sensitive values. Businesses and financial institutions use a TSP to reduce fraud risk, ensure compliance with security standards (like PCI DSS), and streamline secure digital payments across multiple channels (e.g., e-commerce, mobile wallets, IoT).
A TSP also provides connectivity to card networks, handles token updates when card details change, and supports advanced features like network tokens, which improve authorization rates and reduce payment declines. In short, a TSP simplifies secure tokenization at scale, helping businesses protect customer data while optimizing payment performance.
Is a Token Service Provider (TSP) processor-agnostic?
A Token Service Provider (TSP) is typically processor agnostic, meaning it isn't tied to a single acquiring bank or payment processor. Instead, a TSP issues and manages tokens at the network level (e.g., through Visa, Mastercard, or other schemes), making them usable across multiple processors and acquirers. This neutrality gives businesses flexibility to route transactions through different processors without having to re-tokenize customer data. It also provides resilience against processor lock-in, enabling easier switching or multi-processor strategies while maintaining consistent tokenized credentials.
What are the benefits of using a Token Service Provider (TSP)?
A processor-agnostic Token Service Provider (TSP) offers several strategic benefits for businesses managing payments:
- Flexibility and Freedom of Choice: Because tokens can be used across multiple acquirers and processors, merchants aren't locked into a single provider. This makes it easier to switch processors, adopt a multi-processor strategy, or expand into new markets without having to re-tokenize customer data.
- Improved Payment Resilience: Processor outages or performance issues can be mitigated by rerouting tokenized transactions through an alternative processor, minimizing downtime and revenue loss.
- Seamless Customer Experience: Network tokens managed by an agnostic TSP stay valid across processors. If a card expires or is reissued, the token updates automatically, ensuring stored credentials continue working without customer intervention. This reduces checkout friction and declined transactions.
- Operational Efficiency: A single token vault that works with any processor eliminates the need for redundant integrations and token migrations. This streamlines compliance, reduces complexity, and cuts costs associated with maintaining separate token solutions for each provider.
- Future-Proofing: As businesses adopt new payment technologies (digital wallets, IoT, in-app payments), an agnostic TSP ensures consistency and scalability without being limited by a processor's ecosystem or technical roadmap.
In short, a processor-agnostic TSP gives businesses control, continuity, and scalability, protecting against vendor lock-in while enabling optimal routing and customer experience.
Is VGS a Token Service Provider (TSP)?
Yes, VGS is one of the only PSP-agnostic token service providers. This independence allows merchants or enterprises to tokenize payment card data and manage tokens without being locked into a specific payment processing partner.
Ready to enable network tokens?
We have the solution you're looking for. Connect with our team of experts.
Contact Us